DingYuan0118.github.io
Pytorch学习笔记
dataloader与dataset
- dataloader与dataset之间的调用关系如图
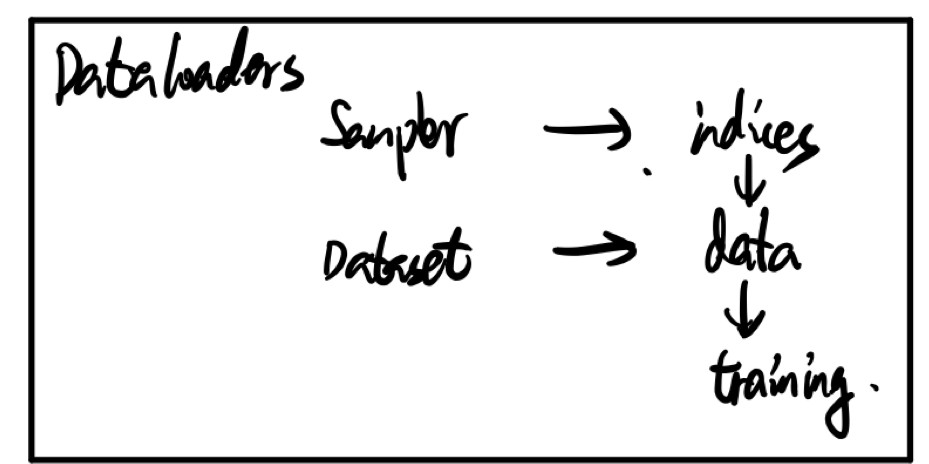
图参考 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/76893455
其中
Sample是iterable对象,其__iter__()方法返回一个iterator对象,torch.utils.data.Dataloader通过调用next(iter(Sample))得到indices。再通过调用dataset[indices]得到数据流。源码如下
class DataLoader(object): ... def __iter__(self): return _DataLoaderIter(self) class __DataLoaderIter(object): ··· def __next__(self): if self.num_workers == 0: indices = next(self.sample_iter) # Sampler batch = self.collate_fn([self.dataset[i] for i in indices]) # Dataset if self.pin_memory: batch = _utils.pin_memory.pin_memory_batch(batch) return batchpytorch 1.0 document,高版本实现更为复杂,但流程相同。
daloader的__len__属性等于该dataloader内部Batch_Sampler的长度。因此,如果自定义Batch_sampler则需要直接指明其__len__属性以便告知一个epoch内需要迭代多少次。如果使用默认的Batch_sampler则其__len__属性值为sampler的__len__属性值除以batch_size,而sampler的__len__属性值等于dataset的__len__属性,因此默认Batch_Sampler的__len__属性值为dataset.__len__除以batch_size。
CUDA的使用
-
pytorch中无论模型的参数还是数据均以tensor的形式存储。tensor的运算均需要运算数在同一设备中,否则将会报错。import torch a = torch.tensor([1,2,3,4], device=torch.device('cuda')) b = torch.tensor([2,3,4,5], device=torch.device("cpu")) c = a + b RuntimeError Traceback (most recent call last) <ipython-input-1-3317b81b183d> in <module> 2 a = torch.tensor([1,2,3,4], device=torch.device('cuda')) 3 b = torch.tensor([2,3,4,5], device=torch.device("cpu")) ----> 4 c = a + b RuntimeError: expected device cuda:0 but got device cpu c = a + b.cuda() c >>>tensor([3, 5, 7, 9], device='cuda:0')
Batchnormal层的使用
具体原理参考Juliuszh的高赞文章
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
针对每个channel,给一组映射参数$\alpha$, $\beta$, 长度为C- num_features - C from an expected input of size
(N,C,H,W) - affine - a boolean value that when set to True, this module has learnable affine parameters. Default:
True - track_running_stats - a boolean value that when set to
True, this module tracks the running mean and variance, and when set toFalse, this module does not track such statistics and uses batch statistics instead in both training and eval modes if the running mean and variance are None. Default:True
import torch import torch.nn as nn w = nn.BatchNorm2d(100) m = nn.BatchNorm2d(100, affine=False) n = nn.BatchNorm2d(100, affine=False, track_running_stats=False) input = torch.randn(20, 100, 35, 45) output_w = w(input) output_m = m(input) print(w.state_dict().keys()) print(m.state_dict().keys()) print(n.state_dict().keys()) print(output_m.size()) print(output_w.size()) >>> odict_keys(['weight', 'bias', 'running_mean', 'running_var', 'num_batches_tracked']) >>> odict_keys(['running_mean', 'running_var', 'num_batches_tracked']) >>> odict_keys([]) >>> torch.Size([20, 100, 35, 45]) >>> torch.Size([20, 100, 35, 45])- num_features - C from an expected input of size
ResNet解析
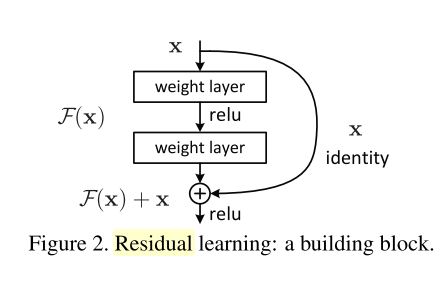
- resnet架构如”Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognitin“所述,由残差块
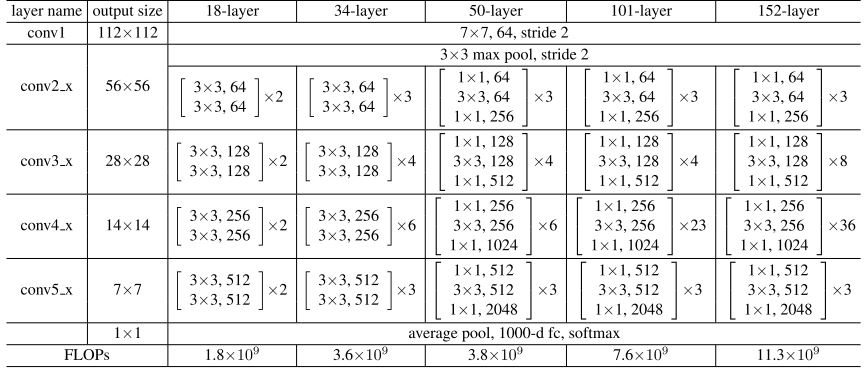
residual block堆叠而成,其具体结构如图所示:其网络整体结构如下:
具体来说,实验使用较多的为
resnet18即18层的resnet。论文中所有resnet均由4个”大”layer组成,每个layer按结构不同又可以由不同数量的block构成。block又由卷积层与batchnorm层组成。block有两种基本结构:BasicBlock与Bottleneck。BasicBlock含有2层卷积层Bottleneck含有3层卷积层
每个卷积层后均使用
batchnorm进行归一化,具体实现可参考pytorch源码
Performance Tuning Guide
- Enable async data loading and augmentation: set the
num_workers> 0, if use GPU traninig, better set thepin_memory=True
-
Disable gradient calculation for validation or inference: use torch.no_grad() context manager
-
Disable bias for convolutions directly followed by a batch norm: if a conv layer followed by a batch norm layer, use
nn.Conv2d(..., bias=False, ....)to disable the bias compute. - Avoid unnecessary CPU-GPU synchronization: When possible, avoid operations which require synchronizations, for example:
- print(cuda_tensor)
- cuda_tensor.item()
- memory copies: tensor.cuda(), cuda_tensor.cpu() and equivalent tensor.to(device) calls
- cuda_tensor.nonzero()
- python control flow which depends on results of operations performed on cuda tensors e.g. if (cuda_tensor != 0).all()
- Create tensors directly on the target device:use
torch.rand(size, device=torch.device('cuda'))instead oftorch.rand(size).cuda()
Parameters与Buffer的区别
parameters记录反向传播时需要optimizer更新的参数buffer记录反向传播时不需要optimizer更新的参数
二者均记录至model.state_dict()方法中,state_dict()返回一个OrderedDict,其中存储着模型的所有参数.
register_parameter()与register_buffer()用于将自定义的参数手动添加至OrderedDict中
常用画图函数
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot(imgs, with_orig=True, row_title=None, **imshow_kwargs):
if not isinstance(imgs[0], list):
# Make a 2d grid even if there's just 1 row
imgs = [imgs]
num_rows = len(imgs)
num_cols = len(imgs[0]) + with_orig
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=num_rows, ncols=num_cols, squeeze=False)
for row_idx, row in enumerate(imgs):
row = [orig_img] + row if with_orig else row
for col_idx, img in enumerate(row):
ax = axs[row_idx, col_idx]
ax.imshow(np.asarray(img), **imshow_kwargs)
ax.set(xticklabels=[], yticklabels=[], xticks=[], yticks=[])
if with_orig:
axs[0, 0].set(title='Original image')
axs[0, 0].title.set_size(8)
if row_title is not None:
for row_idx in range(num_rows):
axs[row_idx, 0].set(ylabel=row_title[row_idx])
plt.tight_layout()
如何快速对模型指定层进行操作?
通过将func 与 model.apply 方法联合使用,可以达到对网络中同一类别的层进行指定操作。
-
以将训练时网络中所有
BN层的training属性置为False为例import torch.nn as nn def freeze_bn(m): if isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d): m.eval() model.apply(freeze_bn)model.apply(func)方法会将func递归地对每个子模块进行调用,从而实现将所有BN层的training属性置为False。同理,可使用import torch.nn as nn def activate_bn(m): if isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d): m.train() model.apply(freeze_bn)将模型所有
BN层的training属性重新置为True。